Soil testing and nutrient analysis are foundational to optimising nutrient management for healthy, high-yield crops. This practice not only enhances soil health but also ensures sustainable fertiliser use. Let’s explore the importance and key aspects of soil testing and nutrient analysis:
Soil testing provides valuable insights into the current nutrient levels, including essential macronutrients and micronutrients. By tailoring fertiliser recommendations to specific crop needs, soil testing prevents fertiliser over-application, reduces costs, and minimises environmental impact.
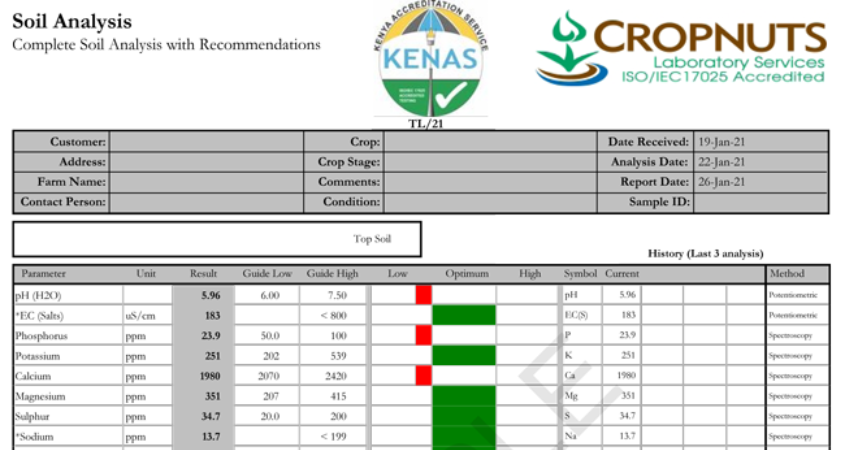
Soil testing measures macronutrients like Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), Potassium (K), Calcium (Ca), Magnesium (Mg), and Sulphur (S), guiding the selection of appropriate fertilisers for optimal crop growth. It also evaluates essential micronutrients such as iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), zinc (Zn) and others, which, despite being needed in smaller quantities, are crucial for overall plant productivity.

Accurate soil testing begins with sample collection, ensuring samples are taken from multiple field locations for proper representation. Samples are sent to an accredited laboratory to analyse nutrient levels, pH, organic matter content, cation exchange capacity (CEC), and other parameters. Results are interpreted to identify nutrient deficiencies or excesses, forming the foundation for precise fertilisation strategies.
Tailoring fertilisation based on soil test results enhances fertiliser use efficiency, reducing over-applications and minimising environmental impact. This targeted approach allows farmers and agronomists to cut fertiliser input costs while maintaining or increasing yields.
Soil testing includes pH measurement, which determines soil acidity or alkalinity. Since pH affects nutrient availability, correcting it is crucial. Lime may be recommended to raise pH in acidic soils, improving nutrient accessibility to plants.
Regular soil testing, typically conducted annually or before each planting season, helps monitor changes in soil fertility and nutrient levels over time. Testing should align with crop rotation cycles to ensure accurate recommendations for the upcoming crop.
In conclusion, understanding the significance of soil testing and nutrient analysis is vital for making informed nutrient management decisions. Regular soil testing, accurate interpretation of results, and customised fertilisation ensure sustainable soil health, optimal crop yields, and efficient resource use while minimising environmental impact.
For personalised soil testing insights and tailored fertilisation strategies, contact our experts at support@cropnuts.com.
Grow more with less
#agronomy #soilhealth #soilscience #sustainability #agriculture
Order our services and get to know how to improve your soil for better yeilds.