
Copper (Cu) is a vital micronutrient that plays a crucial role in plant growth and development. Although required in trace amounts, copper has a significant impact on crop health and productivity. Let’s explore the importance of copper in plant nutrition and how to manage it effectively to ensure optimal crop performance:
Copper is critical in the photosynthesis process. It also plays a key role in lignin synthesis, which is essential for strengthening plant cell walls. Copper is involved in several enzyme functions that are crucial for respiration, carbohydrate metabolism, and the synthesis of proteins and antioxidants, which help plants withstand environmental stress.
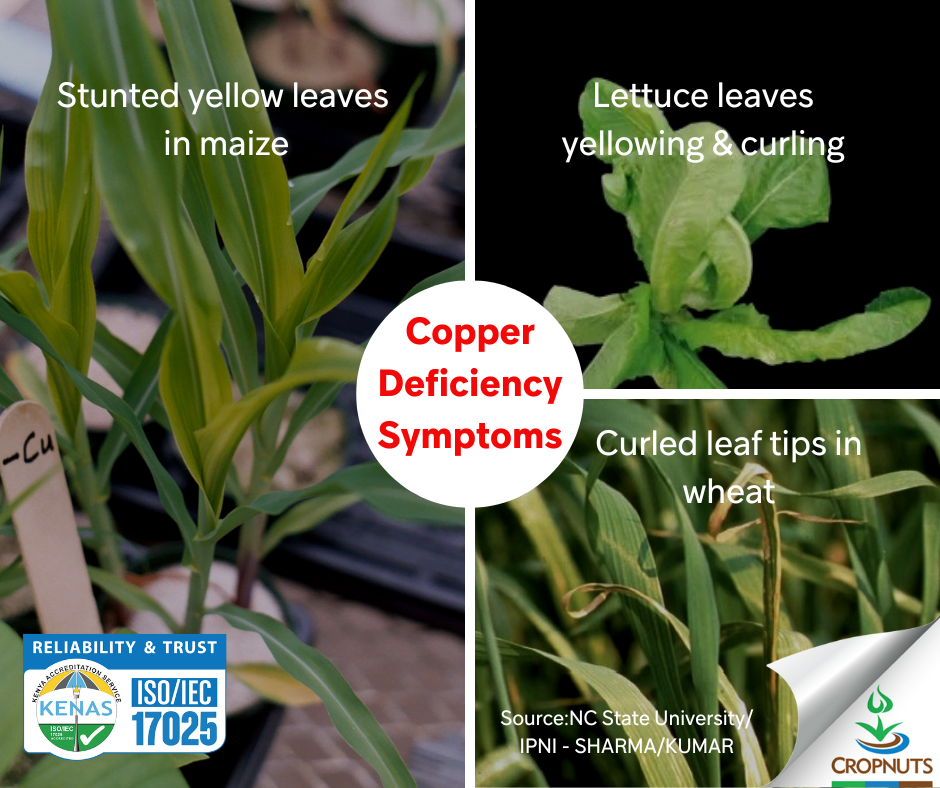
Copper deficiency in plants often manifests as stunted growth and delayed maturity. Young leaves may exhibit dark green or bluish-green coloration, curling, and twisted tips. In cereals like wheat, copper deficiency cause dry, white and twisted or curled leaf tips (white tip). Early detection and correction are essential to prevent significant yield loss and ensure healthy plant development.
Copper availability in soils can be influenced by several factors, including soil pH, organic matter content, and soil texture. High soil pH (alkaline conditions) can reduce copper solubility, making it less available to plants. Soils with high organic matter can bind copper tightly, also reducing its availability. Sandy soils with low organic matter content are more prone to copper deficiency due to leaching.
Regular soil and plant tissue testing is essential to monitor soil copper levels and guide fertilization practices. Applying copper sulfate or copper foliar sprays can effectively address copper deficiencies. Incorporating organic matter can enhance soil structure and microbial activity, potentially increasing copper availability. However, care should be taken as excessive organic matter can bind copper. Maintaining an optimal soil pH (slightly acidic to neutral) can help improve copper solubility and uptake by plants.
In conclusion, understanding and managing copper nutrition is vital for maintaining healthy crops and achieving high yields. By regularly monitoring soil copper levels and adopting best management practices, farmers and agronomists can ensure their crops receive the copper they need for robust growth and resilience. For personalized guidance on managing copper and safeguarding your crop yield, feel free to contact our experts at support@cropnuts.com.
Grow more with less
#savesoil #soilhealth #soilscience
Order our services and get to know how to improve your soil for better yeilds.